Home » Posts tagged 'Moral Compass' (Page 19)
Tag Archives: Moral Compass
The Pathology of Praise
 You’re so cute. You’re so sweet. You’re such a doll.
You’re so cute. You’re so sweet. You’re such a doll.
You slob. You moron. You’re such a loser.
Anyone who has studied education or taken parenting classes has heard the eight-to-one rule: offer eight positive comments for every negative one. The theory is sound. By responding to good behavior, we accomplish three things:
- reinforce that behavior so it will be repeated more often
- encourage a positive self-image inconsistent with bad behavior
- legitimize occasional criticism so it will be taken to heart
All well and good. Except when it doesn’t work.
In her acclaimed bestseller, Mindset, Dr. Carol Dweck reports that grade school teachers criticize boys eight times more often than girls. If that weren’t enough, school-age boys typically pepper their conversation with insults, put-downs, and name-calling. Consequently, we should expect to find that girls grow up into self-confidant over-achievers and boys grow up into meek underperformers.
In fact, just the opposite is true.
Professor Dweck observes that the constant negativity directed at boys makes them increasingly impervious to criticism, which may boost their confidence but leaves them unreceptive to constructive advice. In contrast, the praise lavished on girls can leave them hypersensitive to criticism, to the point where they are afraid to take risks and tend to indulge in constant self-doubt.
Applied to society at large, this may explain a lot about our collective cultural dysfunction.
Down with Democracy?
 AMERICANS AGAINST HATRED AND BIGOTRY.
AMERICANS AGAINST HATRED AND BIGOTRY.
DUMP TRUMP.
NOT MY PRESIDENT.
[EXPLETIVE] UR WALL.
WE WON’T GIVE UP. WE WON’T GIVE IN.
UNITED WE’RE STRONGER (you have to love the irony).
These are just a few of the slogans that bedecked the nation-wide protests against Donald Trump’s electoral victory, i.e., against the American democratic system. Accompanying images included swastikas and pictures of Adolf Hitler.
Of course, protest is a fundamental part of our democracy, guaranteed by the First Amendment (which, incidentally, many Yale students petitioned to repeal). But protest is only productive when it advocates a viable solution to a problem. When protest is nothing more than collective whining, it easily turns into mob violence — indeed, as it did in several instances.
So what do the protesters actually want? To repeal the democratic process? To overthrow a legally elected chief executive? Public lynching?
If they want to advocate dismantling the electoral college, they might find support on both sides of the aisle… but only for the next election cycle. And they could make their point without vandalism, arson, or public obstruction.
On the other extreme, you have college students so traumatized by the election results they have requested exemptions from classwork and midterm exams. Such fragility does not bode well for the future leadership of the country.
It’s a pity we can’t conjure up an alternative reality portal; it would be amusing to get a glimpse of how the anti-Trump contingent would be reacting — had the election gone the other way — to disgruntled Trump supporters protesting the “rigged” election that stole victory from their candidate.
But one does have to acknowledge that sometimes the left is right. One protest sign manages to say it all:
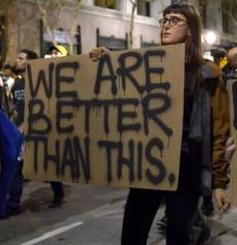
How we move forward
 Too many voters held their noses yesterday as they entered the polling booth to vote for the candidate they considered least toxic. A smaller number could only make peace with their conscience by voting for some unexceptional third-party candidate. Then there were those who couldn’t bring themselves to vote at all.
Too many voters held their noses yesterday as they entered the polling booth to vote for the candidate they considered least toxic. A smaller number could only make peace with their conscience by voting for some unexceptional third-party candidate. Then there were those who couldn’t bring themselves to vote at all.
Will the country survive this winter of our discontent? Only time will tell. But the question that lingers in the aftermath of electoral acrimony is this: are we going to start this all over again in two more years?
Sadly, we just might. Back in January, David Gelertner proposed in the Weekly Standard that the problem with the political left is that liberalism has become their new religion. For most people, religion is not a rational but an emotional commitment that emerges from some amorphous inner voice or feeling. And when people cannot defend their religious beliefs intellectually, they lash out with disproportionate ferocity at anyone who challenges those beliefs. Mr. Gelertner argues that the irrational dogmatism of many liberals bears less resemblance to political discourse and more to the religious fervor of blind faith.
He’s right, of course. But he’s wrong when he contends that this is overwhelmingly a phenomenon of the left.
4 Lessons for Successful Leadership
(Expanded from a previous article.)

Tom Hanks’s recent movie “Sully” allows us to re-experience the dramatic events of January, 2009. Looking back, there are three great stories in the averted disaster of US Airways Flight 1549 that can change our outlook on life’s unexpected twists and turns.
First is the story of providence, which placed a pilot with precisely the right training, experience, and temperament at the helm of the crippled jetliner while placing the aircraft within reach of the only feasible landing strip — the Hudson River — for a safe, if chilly, touchdown.
Lesson 1: Even when things go wrong, look for an unexpected solution at hand to make them go right.
Second is the story of heroism. The pilot, Chesley Sullenberger, drew upon his experience with both military fighters and gliders to bring the passenger plane safely down from the sky. The flight crew quickly and efficiently instructed the people to prepare for impact and then hastened them off the sinking plane. The rescuers, both professional and private citizens, steered their craft to the crash site within minutes. Not one life was lost.
Lesson 2: With the right people ready and waiting, almost anything is possible.
But the third story is that of the passengers. For the most part untrained and unprepared, without exception the passengers on Flight 1549 did precisely what they needed to do in order to survive.
They followed instructions.
Rejecting the new Age of Inevitability
 Isn’t it great to live in an age when machines can do anything? Cars drive themselves, jetliners land themselves, and smartphones do just about everything but tuck us into bed.
Isn’t it great to live in an age when machines can do anything? Cars drive themselves, jetliners land themselves, and smartphones do just about everything but tuck us into bed.
Recognition software can read our moods and even catch us telling lies. (That’s a good thing, right?) Programs can analyze our handwriting and predict our likes, dislikes, and likely actions by tracking our digital footprints. Soon, Amazon may be filling orders for us that we haven’t even placed yet.
In the workplace, software programs may start deciding who gets hired or promoted based on models constructed from data gathered about the highest performing employees. This may include variables based on medical history, psychological markers, and virtual clues to everything about us including age, gender, political leanings, and sexual preference.
In a recent Ted Talk, Zeynep Tufekci acknowledges that these programs may make decisions more objectively than humans do. But she cautions that machines trained to infer and predict are only as good as their programming, and will of necessity reflect the biases of their programmers — which could mean compounding, not eliminating, bias.
What’s more, the algorithms that produce this kind of “machine learning” don’t allow for human insight and intuition. It’s all statistical analysis, which turns probabilities into absolutes with no assessment by human reasoning and without allowing room for appeal to a higher authority.
The more troubling issue is our willingness to abdicate the responsibility implicit in free choice. In a culture that has long conflated judgment with judgmentalism, it’s hardly surprising to find how eager people are to reduce every decision to a binary option and thereby eliminate all shades of gray from the mix. And if that’s not enough, we can simply block any information that doesn’t conform to our way of thinking.
My Interview with Bill Martinez
 Listen in on my conversation about political correctness and the culture wars with nationally syndicated radio host Bill Martinez on 10/19.
Listen in on my conversation about political correctness and the culture wars with nationally syndicated radio host Bill Martinez on 10/19.
The War to End all Wars
This Sunday evening, Jews around the world will begin their observance of the week-long festival of Sukkos. There’s much to learn from this celebration that concludes the annual cycle of Jewish holidays. So I’m returning to these thoughts from September, 2001, which remain more relevant than ever.
 Once upon a time there were three little pigs. One built a house of straw, until the big, bad wolf blew it down and gobbled him up. One built a house of sticks, until the big, bad wolf blew it down and gobbled him up. But one built a house of bricks and was safe from all the huffing and puffing of the big, bad wolf.
Once upon a time there were three little pigs. One built a house of straw, until the big, bad wolf blew it down and gobbled him up. One built a house of sticks, until the big, bad wolf blew it down and gobbled him up. But one built a house of bricks and was safe from all the huffing and puffing of the big, bad wolf.
Society teaches values to successive generations through its children’s stories. The story of the Three Little Pigs is one of our most enduring fables, teaching the importance of good planning and disciplined effort. But it also carries with it a more subtle message, that safety rests in our own hands and our own labors, that security can be bought for the price of a pile of bricks and a bucket of mortar. This ideal, if it was ever true, went up in flames together with New York City ‘s skyline and Washington’s military nerve center on September 11.
More appropriate now than the Three Little Pigs is Robert Burns’s adage about “the best laid schemes of mice and men.” Indeed, the World Trade Center towers were each designed to absorb the impact of a Boeing 727; what the architects failed to factor in was how the fuel carried aboard a transcontinental airliner would create an inferno capable of compromising the structural strength of steel support beams. Of course, we don’t blame the architects; none of us imagined the acts of incomprehensible evil that brought down those towers.
Which is precisely the point. We cannot imagine the design and the reach of evil. We can make our best effort, erect walls of brick around ourselves and roofs of steel over our heads, but we will never be completely safe. The world is too unpredictable an arena, the mind of the wicked too dark a cavern.
As if to drive home the instability of temporal existence, observant Jews around the world will disrupt their normal lives this week by moving out of their homes into little stick houses to live as our ancestors lived in the desert after their exodus from Egypt. But more than an attempt to recreate the experience of a fledgling nation traveling toward its homeland, the holiday of Sukkos offers us an opportunity to attune our minds to a most fundamental principle of Judaism — that however great our strength and the might of our own hands, however elaborate and well conceived our plans, life strews unexpected obstacles in our path that can scuttle our most certain victories and demolish our most solid edifices.
 A sukkah may be built of virtually any material: wood, brick, steel, canvas, or even string may be used to construct its walls. But no matter how stable or how precarious its walls, the roof of a sukkah must be composed of s’chach, thin strips of wood or leaves, through which the light of the stars can shine at night. And when one sits in the sukkah and looks up at the s’chach — the barest representation of a roof, which will not protect him from even the lightest rainfall — he is inspired by the recollection of his ancestors who trusted in the protection of the Almighty, the One who took them out from under the rod of their oppressors and guided them through the inimical desert before bringing them safely home.
A sukkah may be built of virtually any material: wood, brick, steel, canvas, or even string may be used to construct its walls. But no matter how stable or how precarious its walls, the roof of a sukkah must be composed of s’chach, thin strips of wood or leaves, through which the light of the stars can shine at night. And when one sits in the sukkah and looks up at the s’chach — the barest representation of a roof, which will not protect him from even the lightest rainfall — he is inspired by the recollection of his ancestors who trusted in the protection of the Almighty, the One who took them out from under the rod of their oppressors and guided them through the inimical desert before bringing them safely home.
In his visionary writings, the prophet Ezekiel describes a great battle on the eve of the messianic era, when the all forces of evil in the world combine themselves into a great army called by the name Gog and Magog. The brilliant eighteenth century thinker Rabbi Samson Rafael Hirsch interprets the prophet’s vision not as a military battle but as an ideological war between the philosophy of gog — “roof”– and the philosophy of sukkah, where those convinced that their fate lies in the power of their own hands and their own resources will attack the values of those who recognize the limits of human endeavor to influence the world.
In the immediate wake of the World Trade Center destruction, cries rang out for vengeance and military retribution. Since then, more measured voices have asserted that this war will be like no other, without defined enemies or defined borders, without clear strategies or decisive victories. This is an unfamiliar kind of crisis, where we find our capacity to respond in our own defense or to secure our own future profoundly diminished in a new world order.
So now the citizens and leaders of the world’s last remaining superpower must grapple with the uncertainties of a violent present and a murky future. Some will respond by declaring that we must work harder to take control of our own fate. Others will concede that we will never be secure again. And they will be right: no building, no bunker, no shelter made of brick or concrete or iron will guarantee our safety from the perverse imagination of extremists who can rationalize indiscriminate mass murder.
 Yet for all that, the Jew sitting in his sukkah will look up at the heavens and be at peace. He will recognize that the best laid schemes often come to naught and that, after doing all that can be done, we are best off leaving our fate in the hands of the One who placed the stars in their courses, the One from whom protection ultimately comes for those who trust not in their own strength, but in the source of all strength.
Yet for all that, the Jew sitting in his sukkah will look up at the heavens and be at peace. He will recognize that the best laid schemes often come to naught and that, after doing all that can be done, we are best off leaving our fate in the hands of the One who placed the stars in their courses, the One from whom protection ultimately comes for those who trust not in their own strength, but in the source of all strength.
As the winds of autumn blow with the first hint of winter, we may shiver with cold but never with fear. The illusion of the roof we can see reminds of the invisible reality of the wings of the Divine presence. We neither abandon ourselves to fate nor try to seize hold of it, but turn with confidence to face the future, secure in the knowledge that we have prepared ourselves as best we can to meet whatever life holds in store for us.
Walking in Circles
 As the two contenders for the job of Leader of the Free World continue to confirm our worst fears about their competence and character, it’s worth revisiting these thoughts from 2010 about how we keep ending up in the same place.
As the two contenders for the job of Leader of the Free World continue to confirm our worst fears about their competence and character, it’s worth revisiting these thoughts from 2010 about how we keep ending up in the same place.
“The whole world is a narrow bridge,” taught the great Chassidic master Rabbi Nachman of Breslav (1772 -1810), in one of his most famous aphorisms, “but the main thing is to have no fear at all.”
According to German scientist Jan Souman, however, it seems that we have good reason to be afraid. After exhaustive research devoted to the study of walking, Dr. Souman has amassed a mountain of evidence proving that human beings possess a natural inclination to travel in circles.
Like some impious prankster, Dr. Souman took his subjects out to empty parking lots and open fields, blindfolded them, and instructed them to walk in a straight line. Some of them managed to keep to a straight course for ten or twenty paces; a few lasted for 50 or a hundred. But all of them ended up circling back toward their points of origin.
Not many of them. Not most of them. Every last one of them.
“And they have no idea,” says Dr. Souman. “They were thinking that they were walking in a straight line all the time.”
Dr. Souman’s research team explored every imaginable explanation. Some people turned to the right while others turned to the left, but the researchers could find no discernable pattern. Neither left-handed nor right-handed subjects as a group demonstrated any propensity for turning one way over the other; nor did subjects tested for either right- or left-brain dominance. The team even tried gluing a rubber soul to the bottom of one shoe to make one leg longer than the other.
“It didn’t make any difference at all,” explains Dr. Souman. “So again, that is pretty random what people do.”
In fact, it isn’t even limited to walking. Ask people to swim blindfolded or drive a car blindfolded and, no matter how determined they may be to go straight, they quickly begin describing peculiar looping circles in one direction or the other.
And if, as the research indicates, human brains are hardwired to lead us in circles, why does Rabbi Nachman insist that “the main thing is to have no fear at all”?
 After all, a narrow bridge is a dangerous place to walk in circles.
After all, a narrow bridge is a dangerous place to walk in circles.
Perhaps the answer lies in the words of King Solomon: G-d made man straight, but mankind sought many intrigues (Ecclesiastes 7:29).
The sages teach us that, in his original form, Adam towered above every other manner of creation and radiated a light of spiritual illumination. The inner purity of the First Man shone forth through the physical body that clothed his supernal soul, and the godliness that defined his essence drove him forward in unwavering pursuit of his divine purpose.
But Adam allowed his desire for spiritual elevation to confound his reason, rationalizing that by consuming the forbidden fruit he could internalize the influence of evil and thereby conquer it from within. Despite his noble intentions, by violating the divine word Adam strayed from his straight course and lost himself amidst the winding paths of a crooked world.
The history of Adam’s descendants testifies to the crookedness of man. The moral corruption of the generation of the Flood, followed by rebellion in the formof the Tower of Babel, marked mankind’s steady drift away from the path of Truth. The incipient Jewish nation, even before they had the opportunity to receive G-d’s Law at Sinai, twisted their spiritual yearning into worship of the Golden Calf and condemned themselves to wander directionless in the desert for 40 years.
Only upon entering their land did the Jews have another chance to find their way back to the straight and narrow. But again they lost their sense of purpose, refusing to accept upon themselves a leader who might steer them back on course toward a renewed national mission. And so the prophet declares that, “In those days there was no king; every man did what was upright (yashar) in his own eyes” (Judges 21:25).
The Hebrew word yashar, rendered here as upright, translates literally as straight. Indeed, no matter how much the Jews may have then convinced themselves of the straightness of their path, they were truly wandering in circles.

Dr. Souman explains what might otherwise seem obvious, that there is a simple solution to the circular inclinations of the internal human compass. With external clues, like a mountaintop or other promontory on the horizon, people have no trouble at all traveling a straight line.
Perhaps now we are ready to appreciate the meaning of Rabbi Nachman’s metaphor. We walk through life as if blindfolded, unable to see either the true nature of the world or the true purpose of our existence, bemused by all the material vanities that surround us and vie for our attention. The world is indeed a narrow bridge, with the winds of fad and fancy buffeting us on every side, relentlessly threatening to topple us into the abyss of spiritual oblivion if we place one foot off the path to either side.
But if we raise our eyes above the fray, if we pull the blindfold from our eyes and set our sights upon the mountaintop that beckons us across 3300 years of history, then we can march confidently into the future with no fear of straying from the true course that promises to lead us safely home.
Give a little, get back a lot
 Remember what they taught you when you were a kid:
Remember what they taught you when you were a kid:
It’s better to give than to receive.
Sure, it sounds nice. But no one really believes it.
After all aren’t these our basic assumptions about human nature and the ways of the world?
- No good deed goes unpunished (Clair Boothe Luce).
- When a fellow says, “It is not the money but the principle of the thing,” it`s the money (Kin Hubbard).
- Where large sums of money are concerned, it is advisable to trust nobody (Agatha Christie).
- If you wish to be a success in the world, promise everything, deliver nothing (Napoleon).
- The end of the human race will be that it will eventually die of civilization (Ralph Waldo Emerson).
It may be a cynical way of looking at life, but we had better learn to live with it if we want to get ahead.
Or do we?








